In 2009, Volkswagen launched “The Fun Theory”, an initiative demonstrating how interaction design can drive behavioural change by making everyday activities enjoyable. The campaign, which aimed to promote Volkswagen’s BlueMotion Technologies, aligned with principles of human-computer interaction (HCI) and gamification, showcasing how interactive technologies and design interventions can enhance user engagement and encourage positive habits.
Interaction Design and the Fun Theory
Interaction design (IxD) focuses on crafting experiences that facilitate meaningful interactions between users and systems. By leveraging playful, engaging, and intuitive interfaces, interaction designers aim to influence human behaviour in a positive way. The Fun Theory campaign served as an experiment in persuasive design, proving that fun and interactivity can nudge people toward healthier, safer, and more sustainable behaviours.
The campaign used sensor-based interfaces, auditory and visual feedback, and gamification to transform mundane actions into interactive experiences. Each experiment demonstrated how user engagement with interactive technologies can reinforce positive behavioural patterns.
Case Studies in Interaction and Gamification
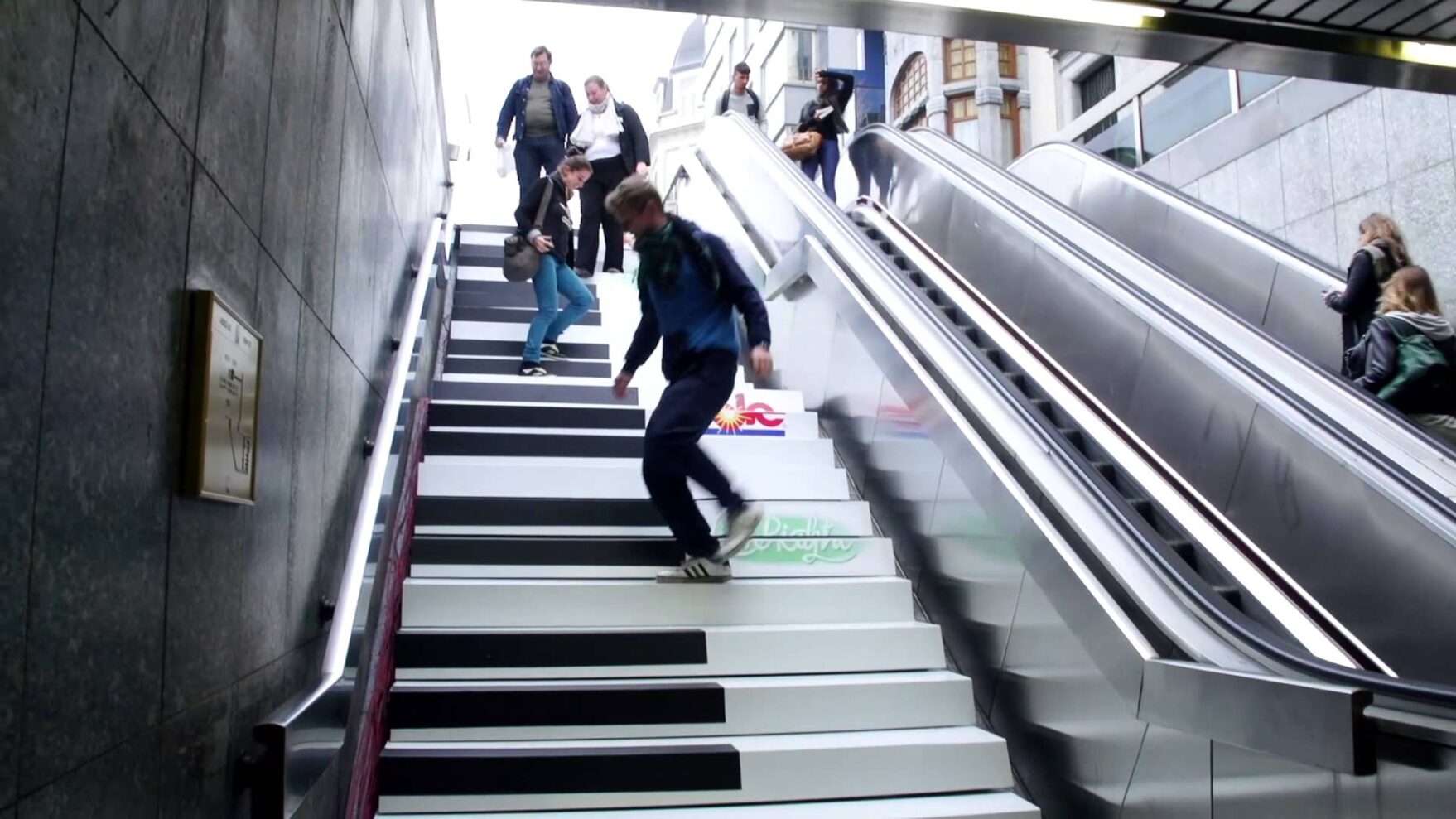
1. Piano Staircase: Encouraging Physical Activity
- Design Concept: Volkswagen transformed a subway staircase in Stockholm into a giant interactive piano that produced sound when stepped on.
- Interaction & Engagement: The system used pressure-sensitive sensors to detect footfalls and generate musical notes.
- Behavioural Impact: The number of people choosing the stairs increased by 66%, highlighting how interactive experiences can promote healthier habits.
🎥 Watch the Video: Piano Staircase
2. World’s Deepest Bin: Reinventing Waste Disposal
- Design Concept: A rubbish bin was equipped with an audio system that played a long falling sound when trash was deposited.
- Interaction & Engagement: The unexpected audio feedback created a playful experience, making litter disposal more engaging.
- Behavioural Impact: The bin collected 72 kg of trash in one day, compared to 41 kg in a standard bin, proving that interactivity can encourage responsible behaviour.
🎥 Watch the Video: World’s Deepest Bin
3. Bottle Bank Arcade: Gamified Recycling
- Design Concept: A recycling bin with arcade-style feedback (lights, sounds, and a scoreboard) was installed.
- Interaction & Engagement: Users were rewarded with game-like mechanics, encouraging repeated engagement.
- Behavioural Impact: Over 100 people used the arcade bin in one evening, compared to only two users for a nearby conventional recycling bin.
🎥 Watch the Video: Bottle Bank Arcade
4. Speed Camera Lottery: Gamifying Road Safety
- Design Concept: A radar camera rewarded law-abiding drivers by entering them into a lottery, funded by fines from speeding motorists.
- Interaction & Engagement: Drivers received feedback in real-time, reinforcing safe driving habits through positive reinforcement.
- Behavioural Impact: Average speeds dropped from 31 km/h to 24 km/h, illustrating how gamification and reward systems can alter behaviour.
🎥 Watch the Video: Speed Camera Lottery
5. Fast Lane: Enhancing Everyday Experiences
Volkswagen introduced ‘Fast Lanes’ to make routine activities more engaging:
- Subway Slide: Users could take a slide instead of stairs, adding excitement to their commute.
- Skateboard Shopping Carts: Shopping trolleys equipped with skateboards made grocery shopping more interactive.
🎥 Watch the Videos:
Key Takeaways for Interaction Design
1. Playfulness Enhances User Engagement
The Fun Theory demonstrated that adding playful interaction to everyday experiences increases voluntary participation and engagement.
2. Gamification Reinforces Positive Behaviour
By incorporating game-like mechanics, such as real-time feedback, rewards, and challenges, interaction designers can create systems that motivate users to adopt better habits.
3. Multisensory Feedback Strengthens Interaction
The use of sound, visuals, and physical response mechanisms heightened user immersion, making interactions more intuitive and memorable.
4. Behavioural Nudging Through Interactive Technology
The campaign exemplified persuasive technology, where subtle environmental changes encourage users to make desirable choices (e.g., taking the stairs instead of the escalator).
5. Real-World Applications in Design
The principles behind The Fun Theory can inform the design of smart cities, public spaces, wearable technologies, and digital interfaces to enhance usability and promote well-being.
Volkswagen’s Fun Theory campaign was more than a marketing initiative; it was a landmark experiment in interaction design and persuasive technology. By integrating play, gamification, and interactivity into urban spaces, the project successfully demonstrated how user experience (UX) design can inspire positive behavioural change.
The campaign remains a powerful case study for interaction designers, UX researchers, and digital transformation experts, illustrating how engagement-driven design can reshape everyday life.











Leave A Comment